Names and roles of the various parts of an injection molding machine, as taught in the 3D model.
- SANKO GOSEI
- Feb 3, 2025
- 3 min read
Injection molding is an essential manufacturing method for the mass production of plastic products. At the heart of the process is the injection molding machine. Injection molding machines have various parts, each of which plays an important role. This article explains the names and roles of the different parts of an injection molding machine in detail, making use of 3D models.
1. basic structure of an injection molding machine
Injection molding machines are broadly composed of three main parts

射出装置(Injection Unit) - The part where the resin is melted and injected into the mold.
型締装置(Clamping Unit) - The part that opens and closes the mold and withstands the pressure during molding.
制御装置(Control Unit) - The part that manages and controls the entire machine.
Let's take a closer look at each of these parts.
1. 射出装置(Injection Unit)
Injection systems are responsible for melting the plastic material and feeding it into the mould. The main components are as follows.
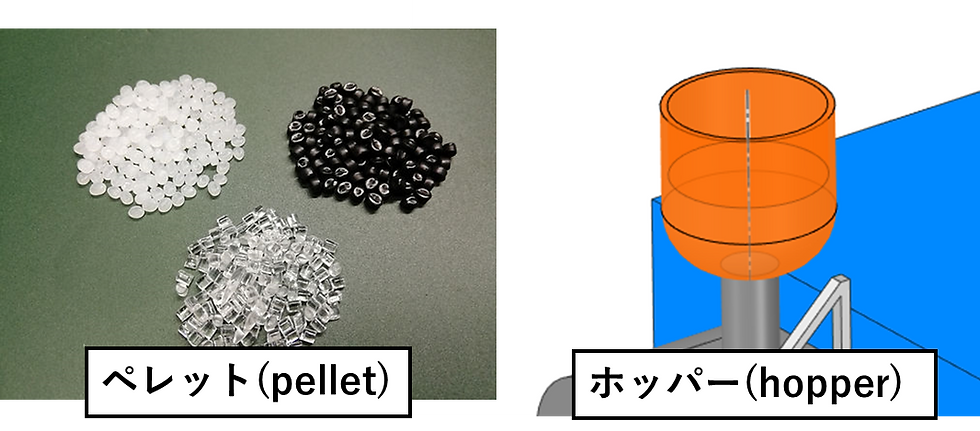
(1) ホッパー(Hopper)
The hopper is the part into which the moulding material (resin in pellet form) is fed. It is usually used in combination with a dryer, and resins that easily absorb moisture (e.g. nylon) are given a drying treatment before being fed.

(2) シリンダー(Cylinder)
The cylinder (also called barrel) is the part where the resin fed from the hopper is heated and melted. Screws are arranged inside to feed the resin forward and melt it evenly.
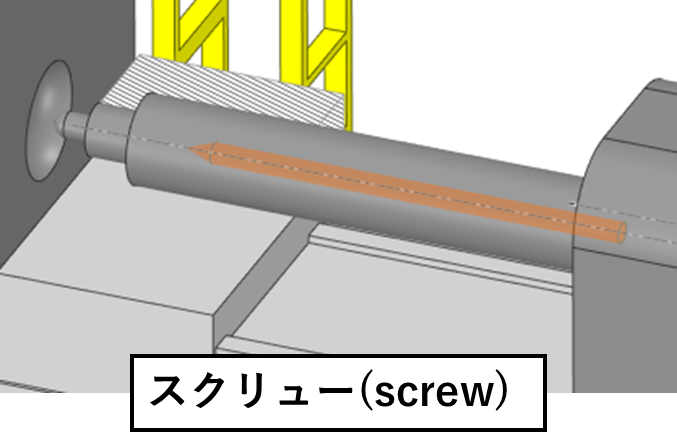
(3) スクリュー(Screw)
The screw is an important component that efficiently melts and kneads the resin. The shape and pitch of the screw largely determines the quality of the moulded product.
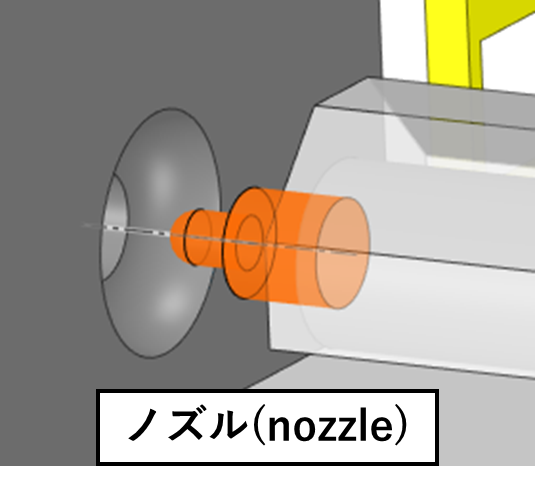
(4) ノズル(Nozzle)
The nozzle is the part that feeds the molten resin in the cylinder into the mould. The nozzle heater regulates the temperature and ensures the fluidity of the resin.
2. 型締装置(Clamping Unit)
The mould clamping device opens and closes the mould and withstands the high pressure during injection. The main components are as follows.
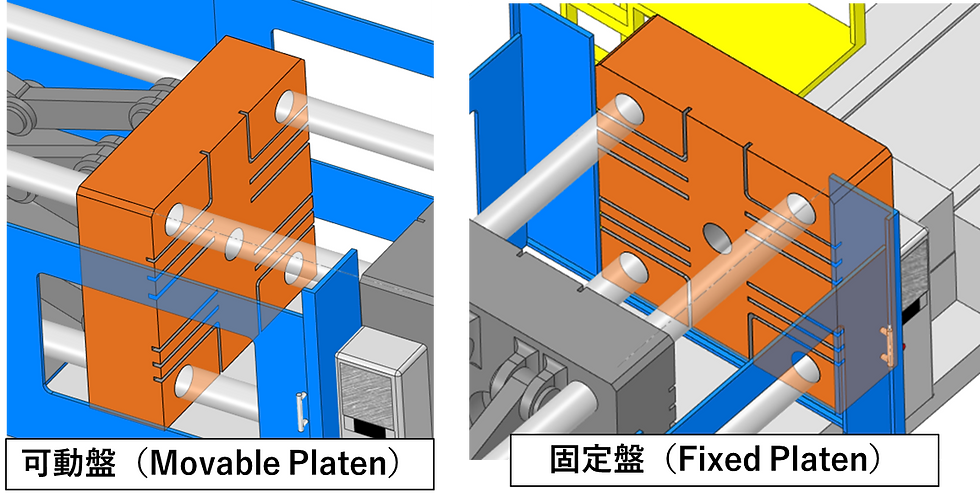
(1) 可動盤(Movable Platen)・固定盤(Fixed Platen)
The mould is installed between the movable and stationary panels. The stationary board is fixed to the machine frame and the mould opens and closes when the movable board slides.
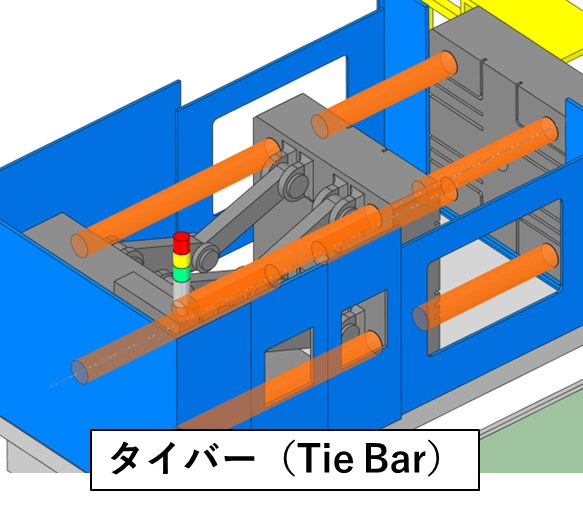
(2) タイバー(Tie Bar)
Tie bars are four strong metal rods that support the movable and stationary panels. They distribute the clamping force evenly and prevent mould deformation.
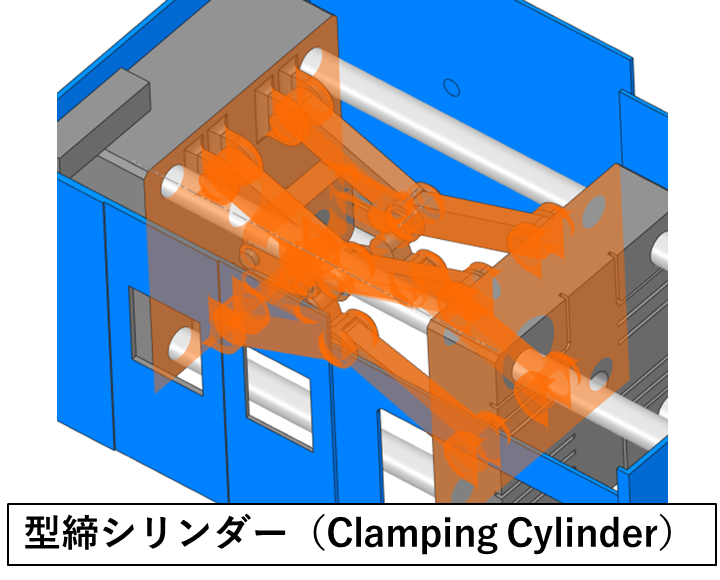
(3) 型締シリンダー(Clamping Cylinder)
The clamping cylinder, either hydraulically or electrically operated, pushes the moving plate into the mould and is responsible for closing the mould firmly. It is important to set the clamping force appropriately to withstand the high pressure during injection.

(4) エジェクタ(Ejector)
This mechanism is used to remove the moulded product from the mould. The ejector pin moves forward and pushes the product out. If the ejector operates improperly, the product may remain stuck in the mould.
Most ejectors are mounted on a movable plate.
3. 制御装置(Control Unit)
The system is designed to manage the operation of injection moulding machines and ensure that moulding is carried out under appropriate conditions.

(1) タッチパネル(Touch Panel)
Injection molding machines in recent years have been fitted with touch screens for operation, allowing the user to set and monitor temperature, pressure, injection speed, etc.
(2) センサー(Sensors)
It is equipped with temperature, pressure and position sensors to acquire data in real time and optimise the moulding conditions.
(3) サーボモーター(Servo Motor)
Electric injection molding machines use servomotors to precisely control the screw and clamping mechanism. They are energy-efficient and contribute to improved accuracy.
4. summary
Injection molding machines are not simply ‘plastic pouring machines’, but precision machines where each part is precisely designed and works together to perform the molding process.
Review of main parts
✅ Injection equipment: hoppers, cylinders, screws, nozzles
✅Clamping devices: movable and fixed panels, tie bars, clamping cylinders, ejectors
✅ Control devices: touch panels, sensors, servomotors.
A better understanding of these components can lead to higher quality moulding. It is particularly important to have a correct understanding of the role of each part when identifying the causes of moulding defects and problems.
While utilising the 3D model, please check and deepen your understanding on the actual machine!










Comments